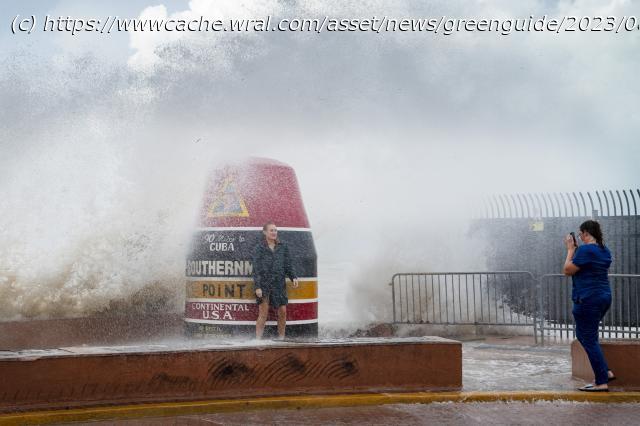
Feeding on some of the hottest water on the planet, Hurricane Idalia is expected to rapidly strengthen as it bears down on Florida and the rest of the Gulf Coast, scientists said. It’s been happening a lot lately.
Feeding on some of the hottest water on the planet, Hurricane Idalia is expected to rapidly strengthen as it bears down on Florida and the rest of the Gulf Coast, scientists said. It’s been happening a lot lately.
“It’s 88, 89 degrees (31, 32 degrees Celsius) over where the storm’s going to be tracking, so that’s effectively rocket fuel for the storm,” said Colorado State University hurricane researcher Phil Klotzbach. “It’s basically all systems go for the storm to intensify.”
That water “is absurdly warm and to see those values over the entire northeast Gulf is surreal,” said University of Miami hurricane researcher Brian McNoldy.
Hurricanes get their energy from warm water. Idalia is at an all-you-can-eat buffet.
“What makes this so tough and so dangerous is” that Idalia is moving so fast and intensifying so rapidly, some people may be preparing for what looked like a weaker storm the day before instead of what they’ll get, said National Weather Service Director Ken Graham.
Idalia “stands a chance of setting a record for intensification rate because it’s over water that’s so warm,” said MIT hurricane professor Kerry Emanuel. On Tuesday, only a few places on Earth had conditions — mostly warm water — so primed for a storm’s sudden strengthening, he said.
“Right now I’m pretty sure Idalia is rapidly intensifying,” Emanuel said.
At the time Emanuel said that, Idalia was clocking 80 mph winds. A couple hours later it was up to 90 mph, and by 5 p.m. Idalia was a Category 2 hurricane with 100 mph winds, having gained 30 mph in wind speed in 15 hours. A storm officially rapidly intensifies when it gains 35 mph in wind speed in 24 hours.
Scientists have been talking all summer about how record hot oceans are at the surface, especially in the Atlantic and near Florida, and how deeper water — measured by something called ocean heat content — keeps setting records too because of human-caused climate change.
Home
United States
USA — mix What makes Idalia so potent? It's feeding on intensely warm water that...