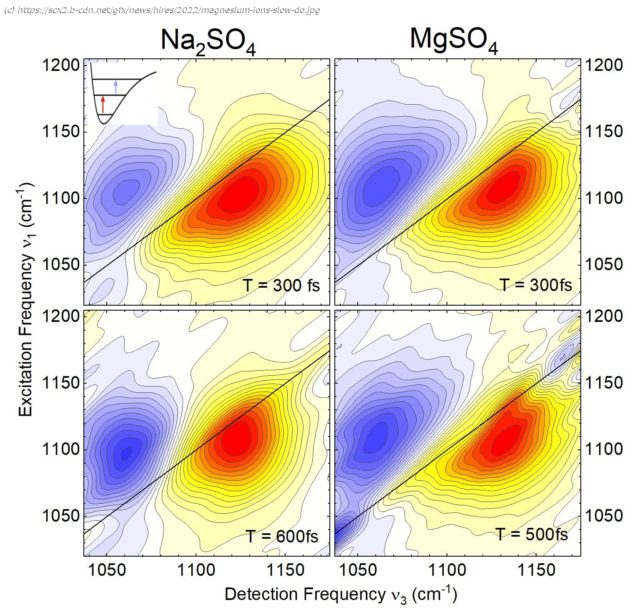
The presence of ions affects the structure and dynamics of water on a multitude of length and time scales. New results from ultrafast spectroscopy and theoretical analyses show that the water environment of specific pairs of magnesium and sulfate ions has a decisive impact on the dynamics of the aqueous solutions.
October 12, 2022
The presence of ions affects the structure and dynamics of water on a multitude of length and time scales. New results from ultrafast spectroscopy and theoretical analyses show that the water environment of specific pairs of magnesium and sulfate ions has a decisive impact on the dynamics of the aqueous solutions.
Liquid water, the native medium for biochemical and cellular processes, consists of a complex network of polar molecules connected by hydrogen bonds. Water responds to the presence of a solute by changing its local structure. The influence of negatively and positively charged ions on liquid water is usually classified via the Hofmeister series which ranks ions based on their ability to structure the water around them or to disrupt the water structure.
The microscopic origin and molecular mechanisms of the Hoffmeister series are controversial, despite many years of research. However, the Hoffmeister series has great relevance because it characterizes the influence ions exert on biomolecules dissolved in water.