The rare metal terbium has been found in an exoplanet’s atmosphere for the first time. The researchers at Lund University in Sweden have also developed a new method for analyzing exoplanets, making it possible to study them in more detail.
The rare metal terbium has been found in an exoplanet’s atmosphere for the first time. The researchers at Lund University in Sweden have also developed a new method for analyzing exoplanets, making it possible to study them in more detail.
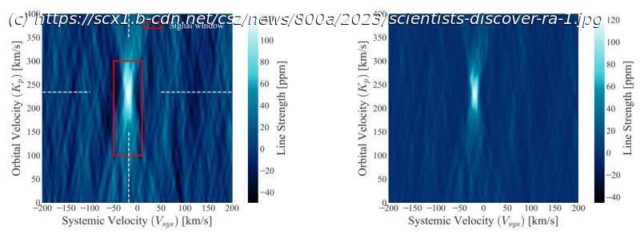
KELT-9 b is the galaxy’s hottest exoplanet, orbiting its distant star about 670 light years from Earth. The celestial body, with an average temperature of a staggering 4,000 degrees Celsius, has since its discovery in 2016 excited the world’s astronomers. The new study, accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics, reveals discoveries about the scalding-hot oddball’s atmosphere.
„We have developed a new method that makes it possible to obtain more detailed information.