Emissions of nitrous oxide—a greenhouse gas more potent than carbon dioxide or methane—continued unabated between 1980 and 2020, a year when more than 10-million metric tons were released into the atmosphere primarily through farming practices, according to a new report by the Global Carbon Project.
Emissions of nitrous oxide—a greenhouse gas more potent than carbon dioxide or methane—continued unabated between 1980 and 2020, a year when more than 10-million metric tons were released into the atmosphere primarily through farming practices, according to a new report by the Global Carbon Project.
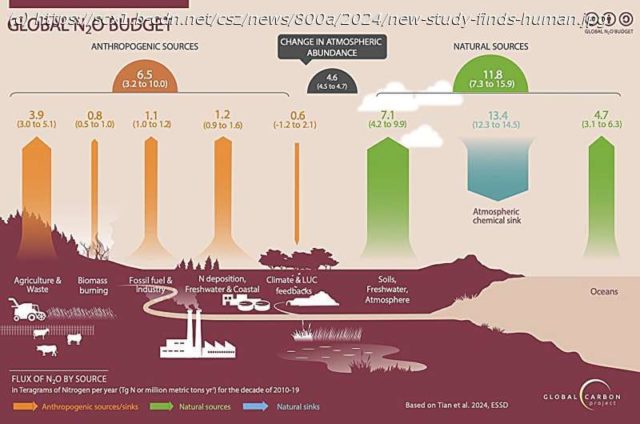
Agricultural production accounted for 74% of human-driven nitrous oxide emissions in the 2010s—attributed primarily to the use of chemical fertilizers and animal waste on croplands—according to the report « Global Nitrous Oxide Budget 2024, » led by researchers from Boston College and published in the journal Earth System Science Data.
In an era when greenhouse gas emissions must decline to reduce global warming, in 2020 and 2021 nitrous oxide flowed into the atmosphere at a faster rate than at any other time in history, the international team of researchers reported. On Earth, excess nitrogen contributes to soil, water, and air pollution. In the atmosphere, it depletes the ozone layer, and exacerbates climate change.
Agricultural emissions reached 8 million metric tons in 2020, a 67% increase from the 4.8 million metric tons released in 1980, according to the study, the most comprehensive study of global nitrous oxide emissions and sinks produced by a team of 58 researchers from 55 organizations in 15 countries.
« Nitrous oxide emissions from human activities must decline in order to limit global temperature rise to 2°C as established by the Paris Agreement, » said the report’s lead author, Hanqin Tian, the Schiller Institute Professor of Global Sustainability at Boston College.
Home
United States
USA — IT Study finds human-caused nitrous oxide emissions grew 40% from 1980–2020, greatly accelerating...