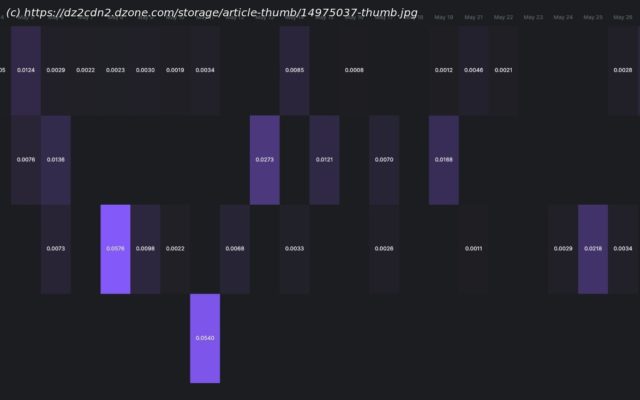
In this tutorial, we will learn how to manage tweet activity using the official Twitter API and generate a heat map from tweets using Arctype. To achieve …
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience. In this tutorial, we will learn how to manage tweet activity using the official Twitter API and generate a heat map from tweets using Arctype. To achieve this, we will be tracking some very popular celebrities’ tweets to create a heatmap like the one in the image above. To fully understand this tutorial, you should have the following: To make use of the Twitter official API, you need to set up your Twitter developer account. Go to https://developer.twitter.com and signup if you haven’t. To sign up, you will need to provide detailed information on how you want to utilize your access to the Twitter API. After providing the information, you will need to wait for Twitter to verify and enable your account. When your account is verified, go to your developer dashboard, as seen in the image above. At this point, you need to create a project which can house multiple applications. First, click on create project, then give your project a name, use case, and a description. Now you need to create an application. To do this, click on create a new app and provide a name for your application. After creating your Twitter application, you will see a page with your application keys, as seen in the image below. Copy and save them somewhere you can easily retrieve them. Go to the Project menu to then open your project. In the apps section, click on the key icon, then generate an access token and access secret token for your application at the bottom of the page displayed. Click on the generate button, then copy and save the access_token and access_secret_token somewhere you can easily retrieve them. To create the Django application, run the following code in your command line: Now, go to the settings.py file and App to the list of installed apps as seen below: Next, go to the urls.py file in the project directory and edit as seen in the code below: Finally, go to the App folder and create a new urls.py file. Add the python code below to the file and save: In the code above, we defined the index URL and connected it to the index view, which we will define in our views.py file. Here we will define the table models in the `models.py` file as see in the python code below: After saving, we need to migrate the database using the below command in the project directory.