Array
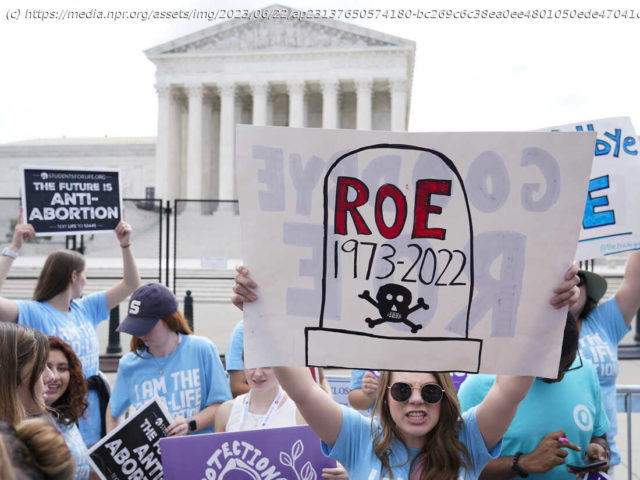
One year after the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, putting an end to the constitutionally protected right to access abortion, the health care landscape has become increasingly fragmented and complex to navigate, spawning widespread confusion.
So far, more than a dozen states have enacted extremely restrictive abortion bans, with the majority making no exceptions for rape or incest. And many more are waiting on legal challenges to make their way through the courts. In Texas, private citizens can sue abortion providers and those who assist patients seeking an abortion after about six weeks of pregnancy.
That has left approximately 22 million women, girls and other people of reproductive age now living in states where abortion access is heavily restricted or totally inaccessible. In the nine months following the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, abortions with providers fell by a monthly average of 2,849 compared to April 2022, new data collected by the Society of Family Planning shows.
With individual states empowered to ban abortion, some health care professionals say they are trapped by poorly drafted laws that criminalize care and fail to consider how women and other pregnant people might inadvertently be affected, including those who had not planned to terminate their pregnancies. Doctors feel trapped by vaguely written bans
«States that have banned abortion are also threatening the health and well-being of people with wanted pregnancies who face obstetric emergency,» Kelly Baden, vice president for public policy at the Guttmacher Institute, told NPR.
«Doctors and hospitals do not know how to operate, or [they’re] operating under a really dark cloud of suspicion and hostility,» Baden added.