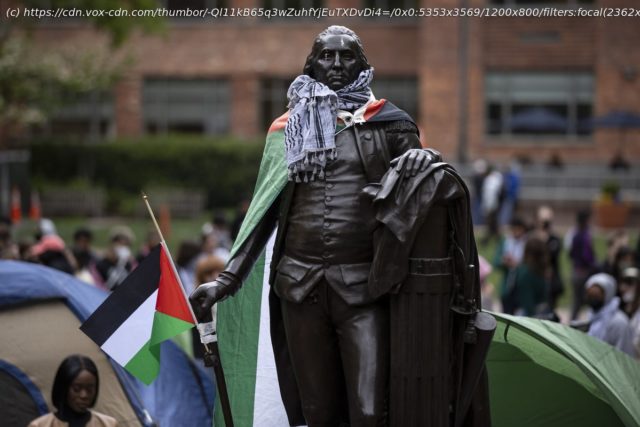
Pro-Palestinian campus protests over Israel’s war in Gaza may be the biggest of the 21st century.
Protests against the war in Gaza have spread to college campuses across the country in the days since students at Columbia University were arrested last week, evoking images of historical student protests that were met with similar backlash.
Recent protests have not yet reached the scale of the major student protests of the late 1960s against the Vietnam War or the 1980s against South African apartheid. But on campus, they may be “the largest student movement so far” of the 21st century, said Robert Cohen, a professor of social studies and history at New York University who has studied student activism. In recent decades, there were mass protests against the Iraq War, as part of the Occupy Wall Street movement, and after the killing of George Floyd, but they were primarily happening off campus.
Just like the protesters that came before them, the students who are now being arrested, and in some cases suspended, for setting up encampments on their campuses in solidarity with Palestinians in Gaza have been demonized by politicians. The vast majority are peaceful protesters who have been overshadowed by a minority of bad actors, some potentially not even affiliated with the universities where these demonstrations are taking place.
Some of their demands, including divestiture from firms that support Israel’s war and occupation, mirror demands that past protesters made to divest from South Africa’s apartheid government. And their discontent has similarly intensified in the face of police crackdowns.
But there are key differences as well. Besides their smaller size, the present-day protests have faced swifter suppression than their predecessors dealt with. In perhaps the most extreme example at the University of Texas-Austin, administrators quickly dispatched police with horses and riot gear absent any signs of violence at a pro-Palestinian protest; charges were later dropped against all 57 arrested. And that signals a deterioration of schools’ commitment to protecting free speech that emerged in the 1960s.
“I think that the fact that this has happened so quickly is unprecedented. And the call for suppression of speech is much more public,” Cohen said.
These protests are only getting started, and it’s too early to tell just how large they might get before classes let out for the summer. But the opposition they’ve faced from their inception could make it harder to build the kind of momentum that their predecessors had — and to achieve their goals. What today’s protests do and don’t have in common with the antiwar protests of the 1960s
Columbia students famously occupied university buildings in 1968 in protest against segregation and the Vietnam War before the police forcibly removed them. They wanted Columbia to end the construction of a segregated gymnasium nearby in Morningside Park and to cut ties with the Institute for Defense Analyses, which was researching weapons development for the US government’s war effort.
This all happened against a backdrop of broader anti-war and anti-racism protests across the US, both on and off campuses, that helped energize the student movement. Student protests swept college campuses in the 1960s, involving thousands of students and hundreds of universities. Those protests remain the biggest in history; the current protest movement is “clearly growing, but it’s nowhere near that scale,” said Angus Johnston, an adjunct professor at the City University of New York studying student protests.
The tactics employed by protesters in the 1960s were also vastly different. While many started and remained peaceful, at their most extreme, students rioted, barricaded themselves in buildings, fought with police, burned down ROTC buildings, and raided draft boards to steal or destroy files. They culminated in the Kent State massacre in 1970, when members of the Ohio National Guard shot at a crowd of unarmed student protesters, killing four and injuring nine.
The recent protests, on the other hand, have not gone anywhere near as far.
“What we are seeing in this spring’s wave of protest is students who are not engaging in property damage. They are not for the most part occupying buildings. They are certainly not initiating physical altercations on any large-scale level,” Johnston said.
Home
United States
USA — mix How today’s antiwar protests stack up against major student movements in history